Our ethical hackers bring decades of real-world experience to the table. They understand the latest attack techniques, threat vectors, and vulnerabilities. With their expertise, we ensure that our penetration tests are rigorous and relevant.
Unlike some providers, we don’t rely solely on automated scans. While scanning tools are essential, they can’t replace human intuition and creativity. We combine advanced scanning technology with the insights of seasoned professionals to provide a comprehensive assessment.
Either we find your vulnerabilities, or the hackers will. Choose CISO Online™ for robust and effective penetration testing services.


Strengthening Cyber Defences with Proactive Assessments. Choose CISO Online™ for robust and effective penetration testing services.




Prevent cyber attacks before they happen
Penetration Testing is a proactive way of assessing the security of your organisation’s IT systems, applications, and infrastructure. A form of ETHICAL HACKING where specialised experts test the strength of your defences and identify any vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious attackers.
Whether it’s hosted in the CLOUD, INTERNALLY, OR EXTERNALLY, we have multiple scenarios to simulate an attacker who might attempt to breach your environment. Our Penetration Testing services will assist your organisation in identifying exploitable vulnerabilities that may be found in your environment.
Want to conduct a pen test?
Crafting Tailor-Made Cyberattack Simulations to defend Your Business Security
Crafting Tailor-Made Cyberattack Simulations to defend Your Business Security
At CISO Online™, we go beyond standard practices by tailoring hacking simulations specifically for your business and industry. Our expert team of ethical hackers possesses extensive real-world experience, ensuring that our penetration tests are as realistic and rigorous as they come.
We distinguish ourselves from other providers by refusing to rely solely on automated scans. Instead, we combine the precision of advanced scanning tools with the expertise of seasoned professionals. This blend of technology and talent ensures a comprehensive assessment, making us the real deal in penetration testing.
Ready to identify your vulnerabilities?



At the forefront of our defence arsenal are state-of-the-art scanning tools, both commercial and open-source, meticulously chosen for their proficiency in uncovering vulnerabilities. Our tools are adept at detecting exposed services, scrutinising application security, and pinpointing open-source vulnerabilities.
To ensure these tools stay a step ahead of evolving hacking tactics, they undergo continual updates. But it’s not just about having the right tools—it’s about the expertise in using them. That’s where our seasoned team comes in, applying their extensive knowledge to wield these advanced technologies effectively.
Getting a Pen Test to find and fix all the vulnerabilities and security gaps in your business is the first obvious step! Let us find the security gaps and the vulnerabilities before hackers find them!
Whether you are looking to meet compliance requirements such as ISO27001 or PCI DSS and want to have a better understanding of your current attack surface, CISO Online™ security experts can assist you in assuring you not only meet those requirements but will validate that your current defence posture holds up against a cyber-attack.
Discovering vulnerabilities is a significant advantage of conducting a penetration test. This allows for fixing the issues before hackers use them. The results of penetration tests can be used to strengthen a company’s security measures. When businesses invest in regular penetration testing, they become less vulnerable to cyber attacks, ultimately saving them money.
After conducting a Pen Test, CISO Online™ will review the integrity of your organisation and implement strategies and frameworks to ensure your data is secure, access permissions are appropriate, and applications are compliant with the latest updates and are free from vulnerabilities.
Additionally, it is crucial that organisations are compliant with regulations, such as ASIC or AUSTRAC, and laws within Australia that define cyber requirements and industry standards within organisations.
We’ve crafted an EXECUTIVE SUMMARY, perfect for Board Reports and non-technical stakeholders. This concise overview is designed to convey the essentials, saving you the effort of distilling intricate technical details into a brief, impactful document for decision-makers.
We deploy state-of-the-art, commercial, and open-source scanning tools, meticulously chosen for their prowess in detecting vulnerabilities, exposed services, and security gaps in applications and open-source components.
To stay ahead in the cybersecurity arms race, these tools are continuously updated to outpace hacker tactics. Our seasoned experts skilfully wield these sophisticated technologies, ensuring comprehensive and effective scanning.
* Harden Your Systems And Reduce Your Organisation’s Risk Exposure By Incorporating Cyber Security Into Your Overall Risk Management Policy.
* Avoid Business Disruption, Escalating Costs, Legal Ramifications, And Reputational Damage That Result From Avoidable Cyber-Attacks And Breaches.
* Independently Validate Your Organisation’s Security Posture And Processes Against Industry Best Practices To Achieve A Competitive Advantage In the Market.
* Provide Feedback On Vulnerabilities Uncovered To Development Teams To Drive Improvements In Secure Coding Practices.
* Achieve And Maintain Compliance Against A Range Of Leading Cyber Security Standards Such As PCI-DSS, ISO27001, NIST And Others.


BLACK BOX PENETRATION TESTING
In a black-box testing assignment, the penetration tester is placed in the role of the average hacker, with no internal knowledge of the target system. Testers are not provided with any architecture diagrams or source code that is not publicly available. A black-box penetration test determines the vulnerabilities in a system that are exploitable from outside the network.
* External penetration testing is another name for black box penetration testing.
* In this method, the pen tester needs to learn about the organisation’s IT infrastructure.
* This process seems more like an experiment of a real-world cyber threat to test the system’s vulnerabilities.
* In this method, the pen testers pretend to be cyberattacks and try to exploit the vulnerabilities.
* This typically takes a long time and can take up to six weeks to finish.
WHITE BOX PENETRATION TESTING
White-box testing falls on the opposite end of the spectrum from black-box testing. penetration testers are given full access to source code, architecture documentation and so forth. The main challenge with white-box testing is sifting through the massive amount of data available to identify potential points of weakness, making it the most time-consuming type of penetration testing.
* Internal penetration testing, clear box, and even glass box penetration testing are other names for white box penetration testing.
* This penetration testing method gives the pen tester full access to the environment, source code, and it infrastructure.
* It is a comprehensive and in-depth pen test examining every aspect, including the application’s fundamental structure and code quality.
* Furthermore, completing this kind of pen-testing approach typically takes two to three weeks.
GREY BOX PENETRATION TESTING
The next step up from black-box testing is grey-box testing. If a black-box tester is examining a system from an outsider’s perspective, a grey-box tester has the access and knowledge levels of a user, potentially with elevated privileges on a system. Grey-box pen testers typically have some knowledge of a network’s internals, potentially including design and architecture documentation and an account internal to the network. The purpose of grey-box pen testing is to provide a more focused and efficient assessment of a network’s security than a black-box assessment.
* The pen tester has limited access to information about the target system’s architecture and source code in this penetration testing method.
* Since the pen tester has limited information about the internal network or web application to work with, they can concentrate on finding and exploiting any vulnerabilities they find.






Let’s identify your security holes before hackers do!
Find out how CISO Online™ can help your organisation empower your CYBER PRESENCE.
| Stage# | Stage Name | Description | Marketing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pre-engagement | Select the systems that need to be tested. | N/A |
| 2 | scop | Forecast time and resources required for the pentest and gather information (test environment details, login credentials and etc.) needed to start the pentest. | Statement of Work |
| 3 | Execution | The system is tested. Daily status updates will be sent. | Statement of Work |
| 4 | Reporting | All pentest findings and issues are reported. | Advertising, content marketing, SEO, social media. |
| 5 | Remediation | Vulnerabilities identified during the pentest are fixed by the project team | |
| 6 | Retesting | Validate the fixes done in the Remediation phase | Vulnerability Report (Update) |

A tailored assessment of your cyber security posture

Tailored packages for SMB's to uplift cyber security

Risk-based approach for large enterprises to uplift cyber security
Penetration testing, also known as pen testing or ethical hacking, is a simulated cyberattack against an organisation's IT systems, networks, or applications. Its goal is to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Penetration testing helps organisations:
Identify and address security vulnerabilities.
Evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures.
Enhance incident response capabilities.
Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Protect sensitive data from potential breaches.
Network Penetration Testing: Focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in an organisation’s network infrastructure.
Application Penetration Testing: Targets web and mobile applications to uncover security flaws.
Wireless Penetration Testing: Assesses the security of wireless networks and devices.
Social Engineering Testing: Evaluates the susceptibility of employees to social engineering attacks, such as phishing.
Physical Penetration Testing: Tests the physical security controls of an organisation, such as locks, badges, and security guards.
Penetration testing should be conducted at least annually. Additionally, tests should be performed whenever there are significant changes to the IT environment, such as new applications, major upgrades, or after a security incident.
Penetration testing should be performed by qualified and certified professionals, often referred to as ethical hackers or penetration testers. These can be internal security teams or external consultants.
A qualified penetration tester should have:
Relevant certifications (e.g., Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)).
Strong technical skills in networking, system administration, and application development.
Experience with penetration testing tools and methodologies.
Knowledge of current cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
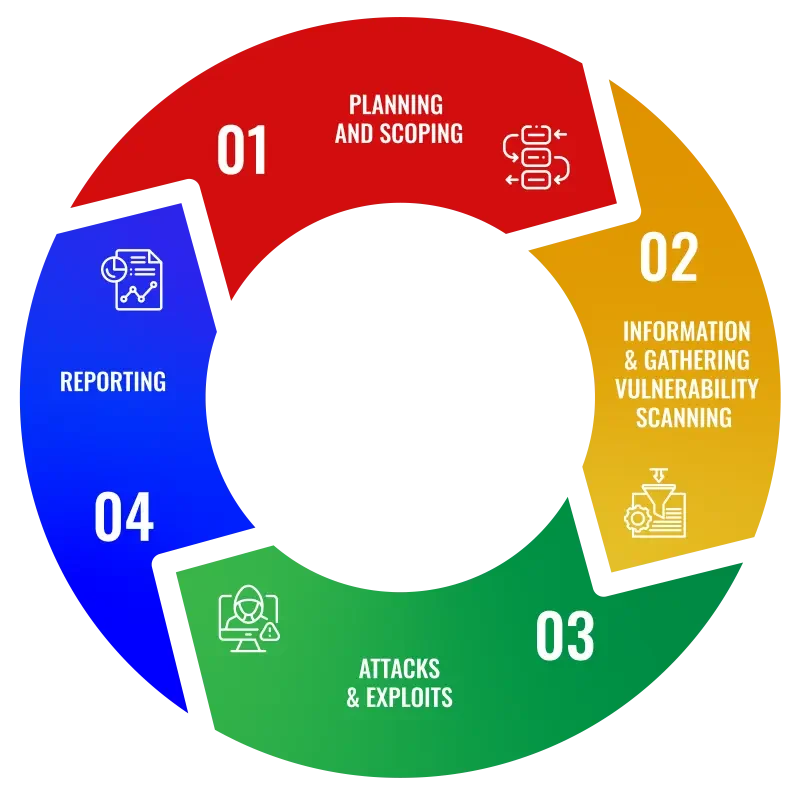
Planning and Scoping: Define the goals, scope, and rules of engagement.
Reconnaissance: Gather information about the target system to identify potential vulnerabilities.
Scanning: Use automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities.
Exploitation: Attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
Post-Exploitation: Assess the potential impact and maintain access if needed.
Reporting: Document findings, including vulnerabilities, exploitation methods, and remediation recommendations.
Remediation and Retesting: Implement fixes for identified issues and retest to ensure vulnerabilities have been addressed.
Scope Restrictions: Pen tests may be limited to specific systems or applications.
Time Constraints: Tests are typically conducted over a limited period, potentially missing some vulnerabilities.
Resource Limitations: Penetration testers may not have the same resources as sophisticated attackers.
False Sense of Security: Passing a penetration test does not guarantee complete security.
Penetration Testing: Involves actively exploiting vulnerabilities to assess their impact. It is a manual and thorough process that provides deeper insights into security weaknesses.
Vulnerability Scanning: Uses automated tools to identify potential vulnerabilities. It is less intrusive and provides a broader overview of potential issues without actively exploiting them.
Define Scope: Clearly outline the systems, applications, and networks to be tested.
Establish Rules of Engagement: Set boundaries and guidelines for the testing process.
Inform Stakeholders: Notify relevant personnel about the test to avoid confusion and ensure cooperation.
Provide Access: Ensure the penetration testers have the necessary access and credentials to perform the test.
Executive Summary: High-level overview of findings and recommendations.
Detailed Findings: In-depth analysis of each identified vulnerability, including severity and potential impact.
Exploitation Evidence: Proof of exploited vulnerabilities, such as screenshots or logs.
Remediation Recommendations: Steps to fix the identified issues.
Methodology: Description of the testing methods and tools used.
Penetration testing helps organisations meet compliance requirements by demonstrating a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating security risks. Many regulations, such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, mandate regular penetration testing to ensure the protection of sensitive data
If not carefully planned and executed, penetration testing can potentially disrupt business operations. However, with proper planning, clear communication, and coordination, disruptions can be minimized. Organisations can schedule tests during off-peak hours and ensure that critical systems have adequate backups.
Objectivity: External testers provide an unbiased assessment.
Expertise: External firms often have specialized knowledge and experience.
Resource Efficiency: Allows internal teams to focus on other tasks while leveraging external expertise for thorough testing.
Advanced Tools and Techniques: External testers may use more advanced tools and techniques, offering a broader perspective on potential vulnerabilities.
Penetration testing, often referred to as a pen test, is a simulated cyber attack against your computer system to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. It's essential for your organisation as it helps in identifying security weaknesses before a real attacker does, allowing you to proactively strengthen your defenses.
Automated vulnerability scanning is a software-based approach that identifies potential vulnerabilities in your systems. Penetration testing, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive approach where a skilled tester actively tries to exploit vulnerabilities in your system, mimicking the tactics of real-world attackers.

